Introduction:
Resistor is one of the fundamental concepts in electronics and is widely used in circuits and electronic devices. This article will introduce the definition of resistor, its working principle, common types, and its significance in practical applications. By gaining a deeper understanding of resistors, readers will better comprehend the role of resistors in circuits and how to choose appropriate resistor components.

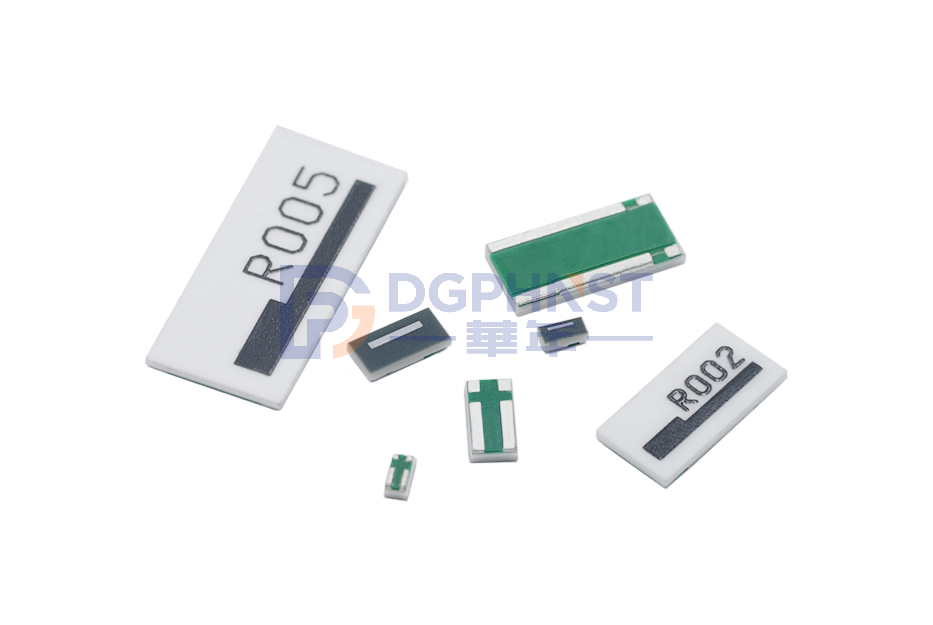
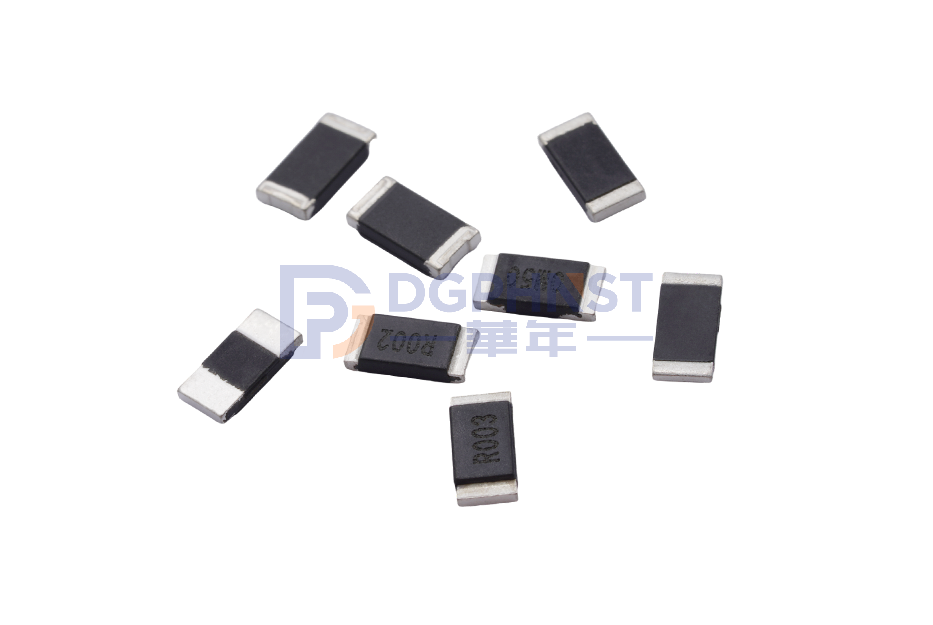
WALTER-STEM
Metal Current Sensing Chip Resistor
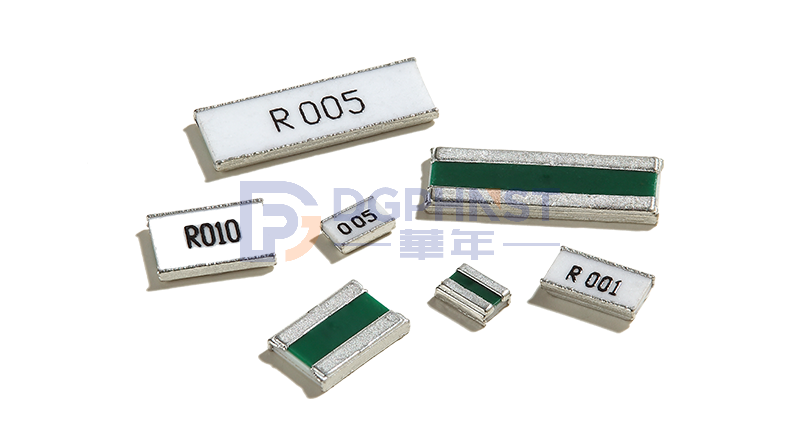

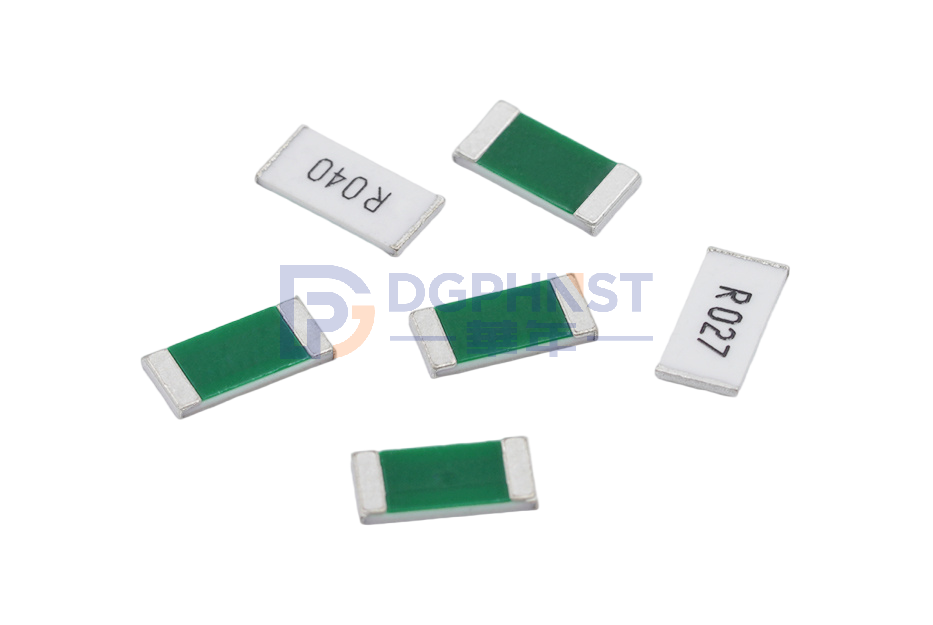
WALTER-HTEM
Wide Terminal Current Sensing Resistor
I. Definition of Resistor:
A resistor refers to a material or device that impedes the flow of electric current. It is the resistance offered by a resistor component to the flow of current and controls the magnitude of the current by increasing the resistance in the circuit. The unit of resistance is ohm (Ω), which represents the degree of resistance to the current.
II. Working Principle of Resistor:
The working principle of a resistor is based on Ohm's law, which states that current (I) is directly proportional to the voltage (V) and inversely proportional to the resistance (R): I = V/R. According to this law, the magnitude of the current is directly proportional to the voltage and inversely proportional to the resistance. When voltage is applied across a resistor, it generates resistance and limits the flow of current.
III. Types of Resistors:
1. Fixed Resistor: Fixed resistors are the most common type of resistors, characterized by a fixed resistance value that cannot be adjusted. Common fixed resistors include carbon film resistors, metal film resistors, and metal oxide film resistors.
2. Variable Resistor: Variable resistors are resistor components that allow for adjustment of the resistance value. By rotating or sliding the controller of a variable resistor, the resistance can be changed, thereby adjusting the current or voltage in the circuit. Common variable resistors include variable resistors, potentiometers, and photoresistors.
3. Temperature-sensitive Resistor: Temperature-sensitive resistors are resistors whose resistance value changes with temperature. Depending on the temperature coefficient of the material, the resistance value of temperature-sensitive resistors varies with an increase or decrease in temperature. Common temperature-sensitive resistors include thermistors and thermoresistors.
4. Photoresistor: A photoresistor is a resistor whose resistance value changes with the intensity of light. Photoresistors are sensitive to light and find wide application in light control and light measurement fields.
IV. Significance of Resistors in Practical Applications:
1. Circuit Control: Resistors are used to regulate the current and voltage in a circuit, controlling the working state and performance of the circuit. By selecting the appropriate resistance value, stable circuit operation, current limiting, voltage division, and other functions can be achieved.
2. Energy Conversion: Between the power supply and the load, resistors play a role in energy conversion. For example, the electrical energy consumed in resistors can be converted into heat energy, which is used in devices such as electric heaters and light bulbs.
3. Signal Processing: Resistors play a crucial role in signal processing circuits. For example, resistors can be used to suppress interference signals in the circuit, achieve signal matching, and provide damping.
4. Temperature Compensation: Some resistor components have temperature compensation characteristics, which can stabilize the circuit performance during temperature changes. This is particularly important in applications that require precise temperature compensation, such as temperature measurement and control systems.
5. Sensor Applications: Many sensors use resistors as their basic components, measuring environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, pressure, etc., by detecting changes in resistance.
Conclusion:
Resistors, as one of the fundamental components in electronic circuits, play a vital role in circuit design and applications. By understanding the definition, working principle, and different types of resistors, we can gain a better understanding of their applications in circuits. Whether it is a