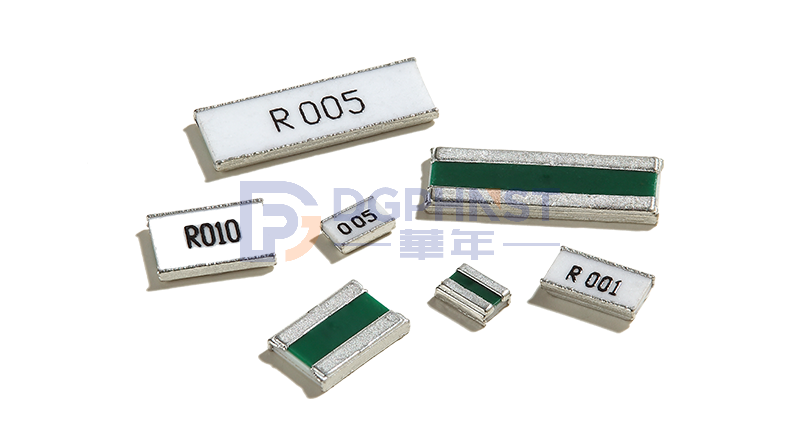
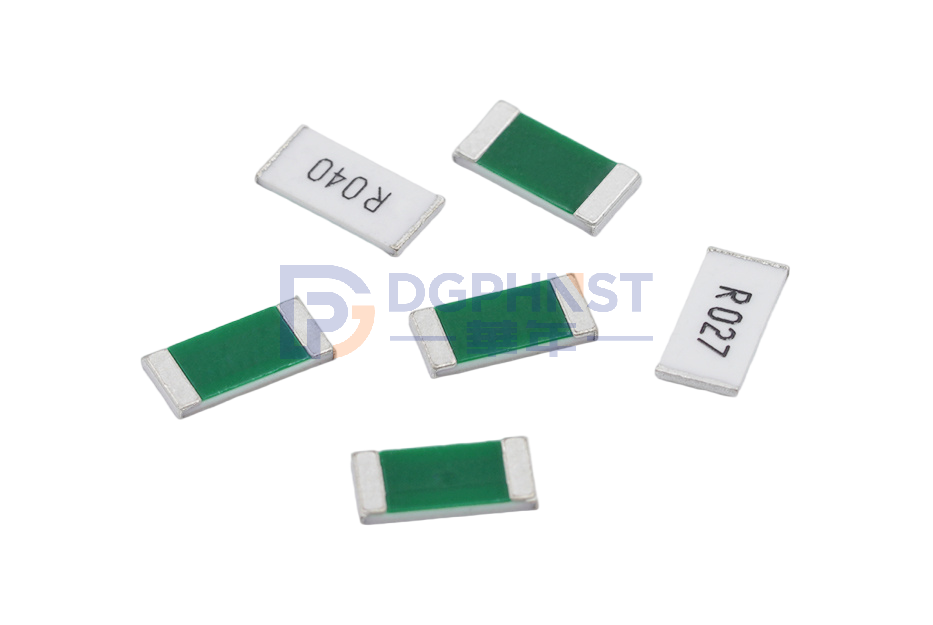
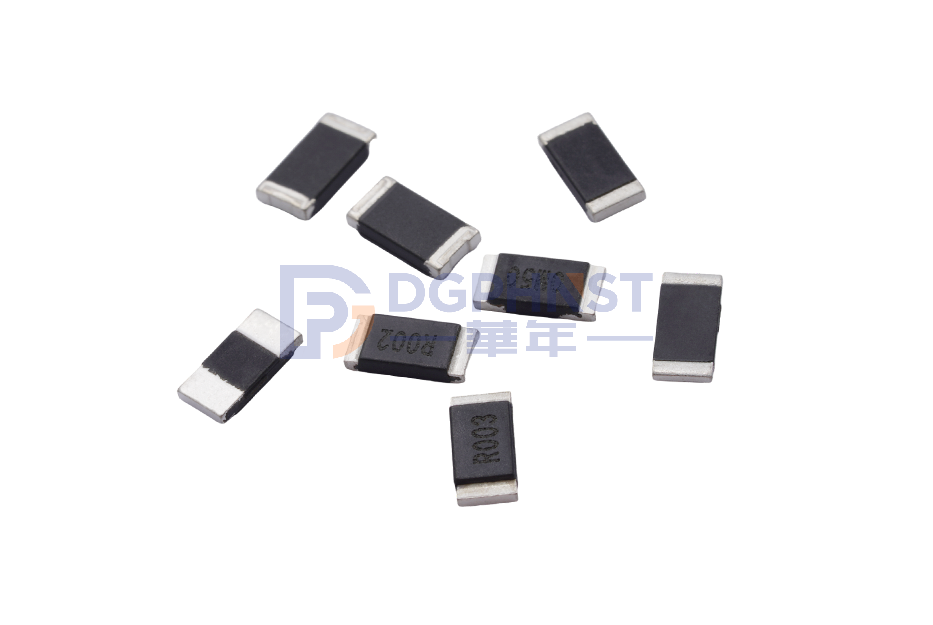
Resistors can be further classified into various types based on their product characteristics. Each type has specific features and applications. Here are some common types of resistors classified based on their product characteristics:
1. hnstshop.com/product-list/R13-p1-l10.html" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Anti-Sulfur Resistor:
Anti-Sulfur Resistors are designed with special materials or coatings to prevent corrosion and damage caused by sulfur-containing gases. They are commonly used in industrial environments where the circuits are exposed to sulfur-related contaminants.
2. Surge Resistor:
Surge Resistors provide protection against transient overvoltage or surge current in circuits. They are frequently used in power equipment, communication devices, and electronic systems where protection against voltage spikes is required.
3. High Power Resistor:
High Power Resistors are capable of handling higher power dissipation and current. They are commonly used in high-power circuits, motor control applications, power supply systems, and electronic devices that require high power handling capacity.
4. Array Resistor:
Array Resistors are resistor devices that combine multiple resistors into a single component. They provide multiple resistance values in a compact package and are used for voltage division, current sharing, and other circuit applications.
5. Automotive Resistor:
Automotive Resistors are specifically designed for automotive electronic systems. They are characterized by high temperature tolerance, resistance to vibration, and moisture resistance to meet the demanding requirements of automotive environments.
6. Shunt Resistor:
Shunt Resistors are used for current sensing and power monitoring applications. They allow measurement of current by sensing the voltage drop across the resistor. Shunt resistors are commonly used in power management, motor control, and electronic devices for current monitoring purposes.
7. Precision Resistor:
Precision Resistors offer high resistance accuracy and stability. They provide precise resistance values and are used in precision measurements, calibration, and precision instrument applications.
8. Low TCR (Temperature Coefficient of Resistance) Resistor:
Low TCR Resistors exhibit minimal changes in resistance with temperature variations. They provide stable resistance values even in environments with significant temperature changes.
9. Thermistor:
Thermistors are temperature-sensitive resistors. Their resistance value changes with temperature, making them suitable for temperature measurement and temperature compensation circuits.
10. Varistor:
Varistors are nonlinear resistor devices that exhibit varying resistance values with changes in voltage. They provide overvoltage protection and voltage clamping functions in circuits.
These are some examples of resistors classified based on their product characteristics. Each type of resistor has specific features and applications. The selection of the appropriate resistor type depends on the specific requirements of the circuit design and application.