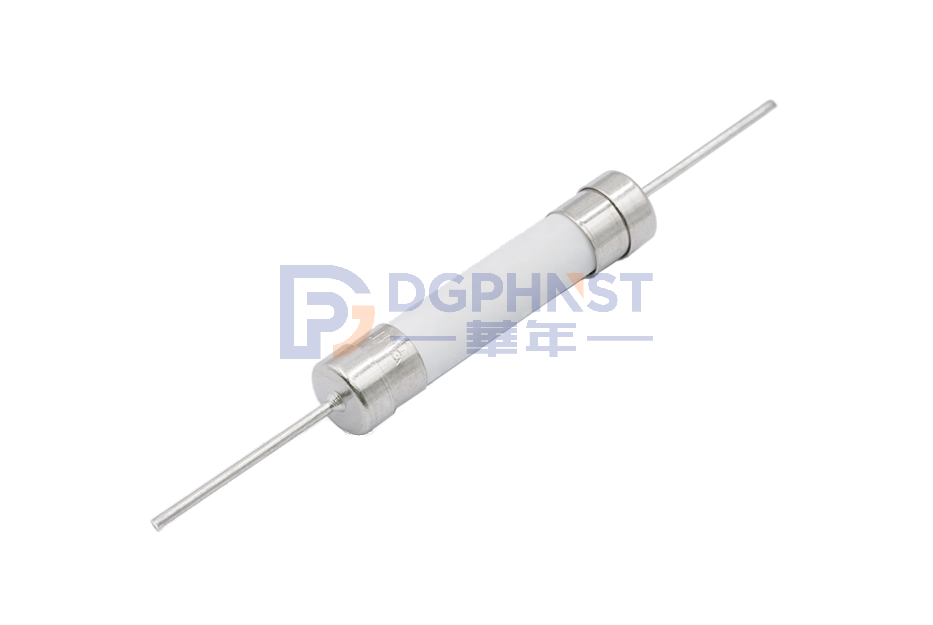
Why do most chargers choose 2A 250V square shell fuses for power supply? Firstly, the 2A 250V square shell fuse is a very common product, while the mains power is 220V, so the voltage must be higher than the mains power, otherwise there will be a large number of product defects. Secondly, the choice of 2A current is due to the overall requirements of the product solution, which involve charging efficiency, grain conversion, etc.

In the power design of chargers, we often find that 2A 250V fuses are widely used. This choice is not accidental, but based on various considerations and the characteristics of power products.
Firstly, from the perspective of the working current requirements of the charger, a typical charger needs to provide appropriate charging current for various electronic devices. In common charging scenarios, its operating current usually does not exceed 2A. Choosing a 2A fuse can ensure stable current flow during normal charging, and quickly melt when the current abnormally increases beyond 2A, protecting the charger and backend equipment.
The rated voltage of 250V takes into account the fluctuation range of the mains voltage connected to the charger. The mains voltage is not always stable at the standard 220V, there may be some fluctuations, and even brief high-voltage pulses may occur in certain special circumstances. The rated voltage of 250V provides sufficient voltage tolerance margin for the charger, ensuring that the fuse can operate stably within the normal range of mains voltage changes without misoperation due to slight voltage fluctuations.
From the perspective of power stability, the internal circuit components of the charger have certain requirements for the stability of current and voltage. A 2A 250V fuse can timely cut off the circuit when the current is abnormal, preventing excessive current from damaging key components such as transformers, rectifier bridges, and filtering capacitors inside the power supply, thereby maintaining stable output of the power supply and ensuring the safety and reliability of the charging process.
Furthermore, considering the usage environment of the charger and the possible fault situations it may face. In practical use, chargers may encounter problems such as short circuits, overloads, etc. When a short circuit occurs at the output terminal of the charger, the current will instantly increase sharply. Without appropriate fuse protection, the strong current may cause internal components of the charger to burn out, and even pose safety hazards such as fire. A 2A 250V fuse can quickly melt in such extreme situations, cutting off the circuit and minimizing losses and dangers.
In addition, cost is also an important factor in choosing 2A 250V fuses. This specification of fuse is readily available in the market at a relatively reasonable price, meeting the protection needs of chargers without significantly increasing their manufacturing costs.
From a compatibility perspective, the 2A 250V fuse is a relatively universal specification that can adapt to most common charger design schemes. This enables charger manufacturers to choose circuit solutions more flexibly in the design and production process, improving production efficiency and product consistency.
In summary, the selection of a 2A 250V fuse for the charger power supply is the result of comprehensive consideration of multiple factors such as the charger's operating current requirements, mains voltage fluctuations, power supply stability, fault protection, cost, and compatibility. This choice can provide effective overcurrent and overvoltage protection for the charger, ensuring safe and reliable operation in various complex usage environments, while also considering the cost and versatility of the product, bringing consumers a stable, safe, and cost-effective charging experience.