Dedicated to the resource recycling and reuse of waste plastics
Murata Production Co., Ltd. has decided to invest in the joint venture company R PLUS JAPAN, which is committed to the recycling and reuse of waste plastics in order to achieve sustainable resource utilization.

In recent years, with the global population growth, social problems such as resource depletion and increased waste have become increasingly serious, requiring enterprises to make efforts in the sustainable utilization of resources.
The goal of the resource recycling and reuse of waste plastics is to establish a plastic recycling mechanism through cross industry cooperation, from raw materials to usage and disposal stages. Our company will promote the resource recycling of waste plastics by participating in this business.
List of participating enterprises
In Vision 2030 and the mid-term policy 2024, Murata Productions has set "sustainable utilization of resources" as an important topic (key topic), and has proposed "sustainable resource utilization rate * 100%" for procurement products and "circular resource regeneration rate * 2 100%" for emissions as goals to be achieved in 2050.(Murata MLCC (GRM), Murata SMT inductor LGQ, LQP)
For example, in 2022, we successfully built a horizontal recycling system for the first time in the electronic components industry, which can reuse PET films used in the manufacturing process of multi-layer ceramic capacitors.
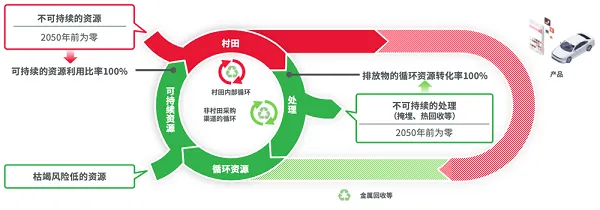
Measures implemented by Murata to achieve sustainable resource utilization
Through this investment as a representative measure, our company will continue to contribute to achieving sustainable society in the future.
Regarding the joint venture company
R PLUS JAPAN Co., Ltd. was founded on June 5, 2020, with its headquarters located in Tokyo. Representing the Chairman of the Board, Yokohiko Yokoi, the company's business mainly focuses on promoting the development and practical application of waste plastic recycling technology.
R PLUS JAPAN, a subsidiary of Murata Productions, is collaborating with American biotech startup Anellotech Inc. to develop environmentally friendly and effective waste plastic recycling technologies. In order to solve the common plastic problem in the world, the company takes "eliminating 'waste' and creating 'future'" as its corporate philosophy. Through cooperation across multiple industries such as plastic recycling and processing, monomer material manufacturing, polymer material manufacturing, packaging container manufacturing, trading companies, beverage and food producers, banks, etc., the company is committed to building a resource recycling mechanism.
Anellotech Inc. is a biochemical startup founded in 2008, headquartered in Pearl River, New York, USA. It has the technology to generate benzene, toluene, and xylene with the same performance as petroleum refining products from non edible plant raw materials.
On the Recycling Technology of Waste Plastic Resources
Currently, most plastic products in Japan, except for plastic bottles, are treated by incineration * 3. This technology is a chemical recycling technology * 4, which can directly reduce general plastic products, including plastic bottles, into raw materials (benzene, toluene, xylene, ethylene, propylene, etc.).
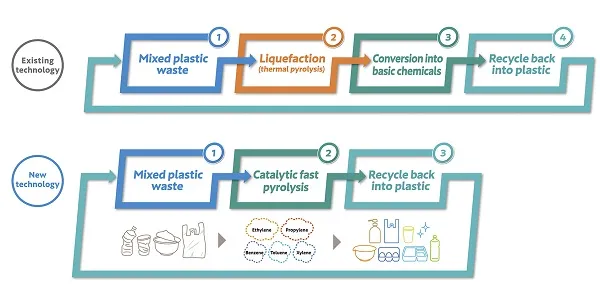
Comparison of Recycling Technologies for Waste Plastic Resources
Compared with traditional recycling through petrochemical processes, this technology has fewer recycling processes and is expected to suppress carbon dioxide emissions and required energy. Once this technology is established, it will be more effective in recycling waste plastics.
Comment:
In the component materials used in the product, firstly, do not use resources with high depletion risk; 2、 Do not use resources prohibited or restricted by stakeholders.
Reuse the emissions generated during the manufacturing process as resources for one's own company or other companies.
Including heat recovery (heat utilization), which involves recovering the heat generated during incineration and using it for power generation and heating.
Transforming the composition of waste resources through chemical reactions before recycling, rather than directly recycling.






