Power semiconductors are the core of electrical energy conversion and circuit control in electronic devices, mainly used to change the voltage and frequency in electronic devices, as well as perform functions such as DC/AC conversion. As long as there is a circuit system with current voltage and phase conversion, power components will be used. Basically, power semiconductors can be roughly divided into two categories: power discrete devices and power integrated circuits. Among them, power discrete device products include MOSFETs, diodes, and IGBTs, among which MOSFETs and IGBTs are the most important.
In the low current region, the conduction voltage of MOSFET is lower than that of IGBT, but in the high current region, the conduction voltage of IGBT is lower than that of MOSFET, especially under high temperature conditions, and this phenomenon is particularly evident. IGBT is usually used with a switching frequency below 20kHz because its switching loss is greater than that of a unipolar MOSFET. The advantage of MOSFET lies in its applicability in the high-frequency field. MOSFET operating frequency can be applied to RF products ranging from hundreds of KHz to tens of MHz, while IGBT reaching 100KHz is almost the optimal operating limit.
MOSFETs have advantages such as high input impedance, low driving power, fast switching speed, no secondary breakdown, wide safe operating range, and good thermal stability. Generally speaking, MOSFETs are suitable for portable rechargeable batteries or mobile devices. As for IGBT, it is suitable for high-voltage and high-power equipment, such as motors, automotive power batteries, etc.
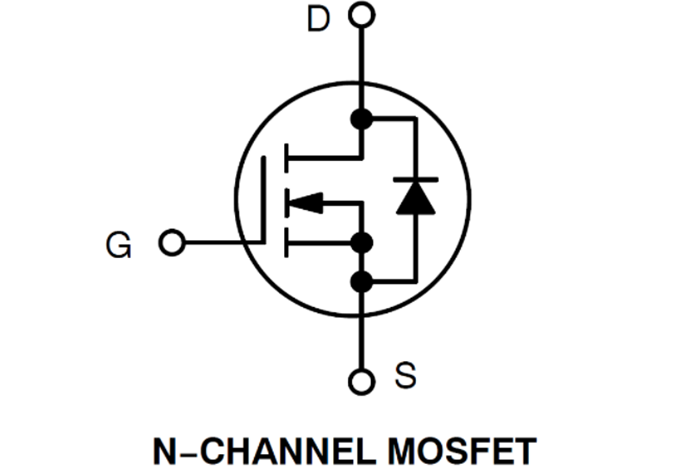
N-channel power MOSFET has lower on resistance and smaller size
With the continuous evolution of MOSFET and CMOS technology, integrated circuits have been rapidly developing since 1960, which is also the reason why the design of power MOSFETs has been realized. The advantages of power MOSFETs are their fast switching speed, high efficiency at low voltages, easy implementation of parallel technology, high bandwidth, robustness, simple bias voltage, easy use, and easy maintenance. Power MOSFETs can be applied in many different fields, including most power supplies, DC-DC converters, low-voltage motor controllers, and many other applications.
Power MOSFETs can be divided into P-channel and N-channel according to their conductive channels. Due to the lower on resistance (RDS (on)) and smaller size of N-channel MOSFETs, their selectivity in product applications exceeds that of P-channel MOSFETs. The application of synchronous rectifiers almost always uses N-channel technology, mainly because the RDS (on) of N-channel is smaller than that of P-channel and can be conducted by applying a positive voltage on the gate.
Most power MOSFETs are carrier devices. N-channel MOSFETs have electron flow during conduction, while P-channel MOSFETs use positive charges called holes during conduction. The mobility of electrons is three times that of holes. Although there is no direct correlation, for RDS (on), in order to obtain equal values, the die size of P-channel is approximately three times that of N-channel, so the die size of N-channel is smaller.
MOSFET driver for motor drive
In motor drive systems, gate driver or "pre driver" ICs are often used in conjunction with N-channel power MOSFETs to provide the high current required to drive the motor. There are many design factors to consider when selecting driver ICs, MOSFETs, and related passive components used in certain situations.
To design a driver for a DC motor (whether it is a brushed motor or a three-phase brushless motor), the design details of the driver should be determined by the characteristics of the motor, with two main factors being the operating voltage and current requirements of the motor. In general, motors have a given rated voltage and rated current, but in actual operation, these values may differ from the rated values. The actual speed of the motor depends on the applied voltage, and the required current of the motor depends on the applied torque. Therefore, the driver design does not necessarily need to fully meet the specifications of the motor.
To ensure that the rated value of the selected power MOSFET is at least equal to the power supply voltage and maximum current required by the motor, it is even better to leave a certain margin to ensure optimal performance. The drain source voltage rating (VDS) of MOSFETs should be at least 20% higher than the power supply voltage. In some cases, especially in systems with high current, large torque step size, and poor power control, the rated current of MOSFET must be high enough to provide the peak current required by the motor.
In addition, heat dissipation is also a key factor in choosing MOSFETs. The dissipated power of MOSFETs generates heat in the drain source resistance RDS (ON), and the thermal conditions including ambient temperature and MOSFET heat dissipation determine the power that can be dissipated. The maximum allowable power consumption is ultimately determined based on the RDS (ON) value of MOSFETs. In addition, it is necessary to consider the total gate charge (QG), which is used to measure the amount of charge required to turn on and off MOSFETs. MOSFETs with lower QG are easier to drive and can switch faster with lower gate drive current compared to MOSFETs with higher QG. Buy electronic components in stock on the Only Sample Mall
Excellent power MOSFET characteristics meet application requirements
Ansenmei is at the forefront of the power MOSFET industry and has launched various specifications of power MOSFETs for different application needs, including N-channel, P-channel, and complementary MOSFETs for power conversion and switching circuits.
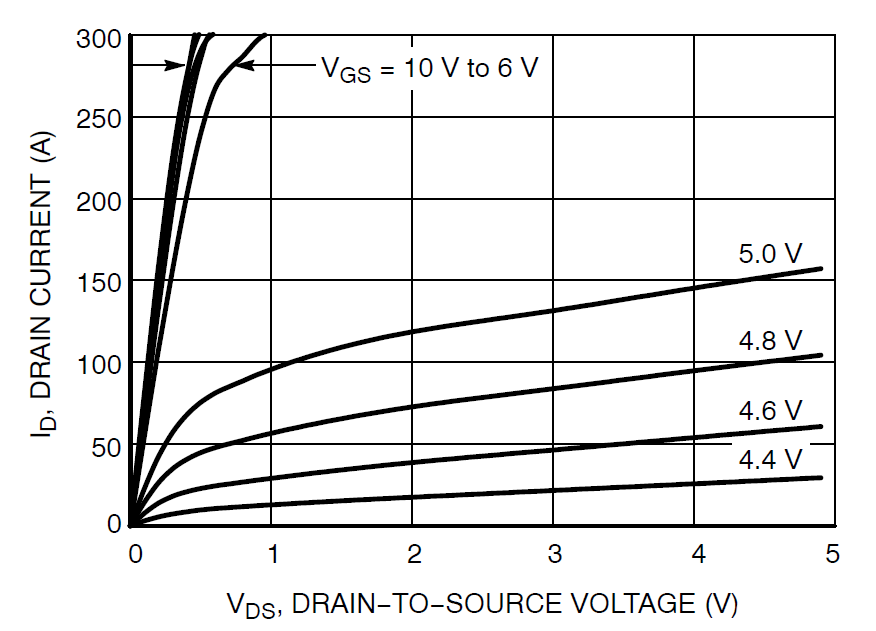
The NTBLS1D5N10MC introduced in this article is a unipolar, N-channel power MOSFET that supports TOLL packaging and can output 100 V, 1.53 m Ω, 298 A power. It has low RDS (ON), low total gate charge (QG), and capacitance, low switching noise/electromagnetic interference (EMI), and is a lead-free, halogen-free/brominated flame retardant (BFR) device that complies with RoHS standards. It can minimize conduction losses and minimize driver losses. It can be applied to electric tools, battery powered vacuum cleaners, drones, material handling, battery management systems (BMS)/storage, home automation and other fields. Common end products include motors. Control, industrial power supply, and solar inverters, etc.
epilogue
The application of motor drive is quite extensive, among which power MOSFET plays an important role. Anson Mei has a diverse range of power MOSFET product lines, among which NTBLS1D5N10MC unipolar, N-channel power MOSFET can meet the stringent requirements of related applications and is one of the best choices for motor drive control.
