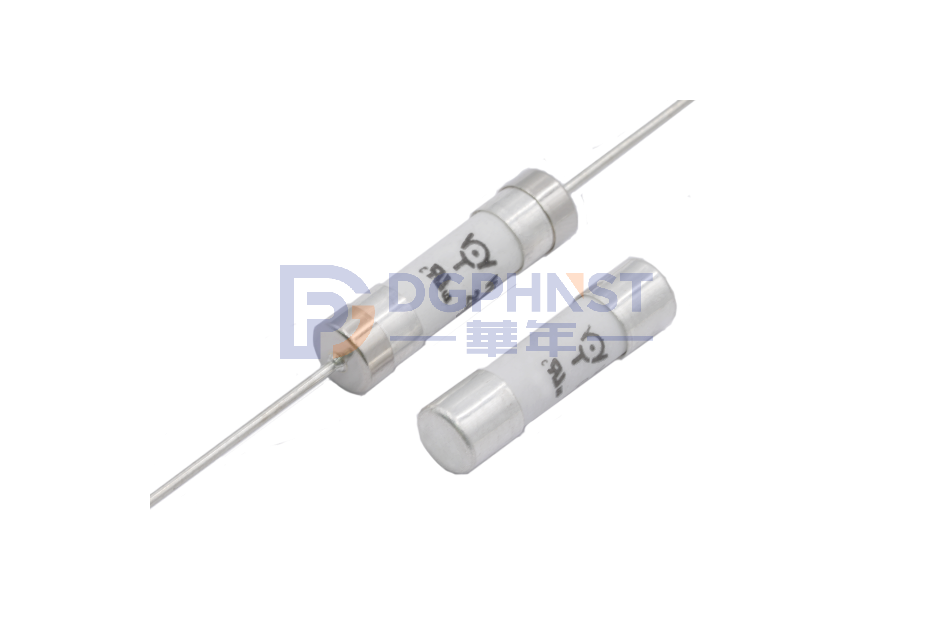
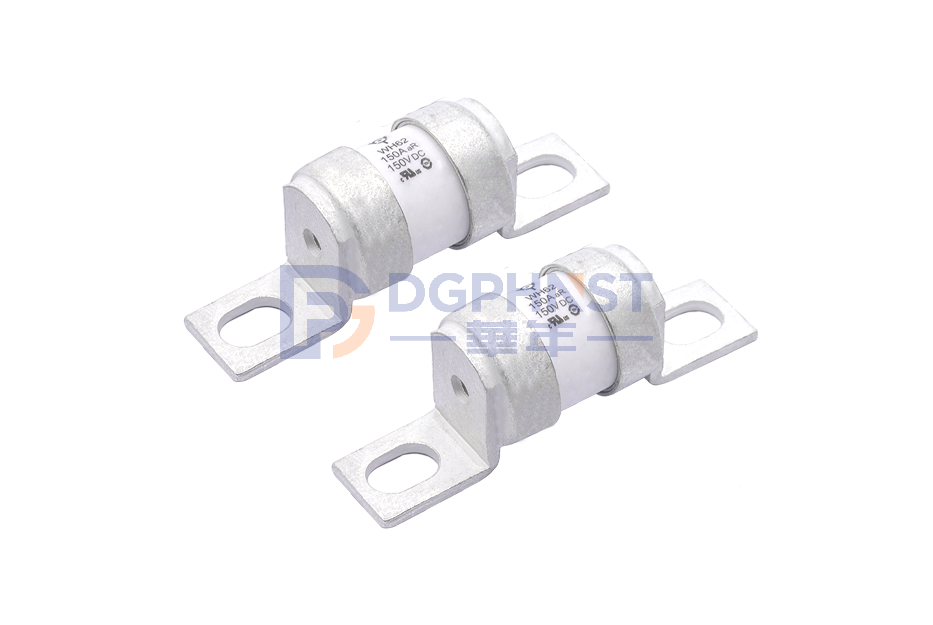
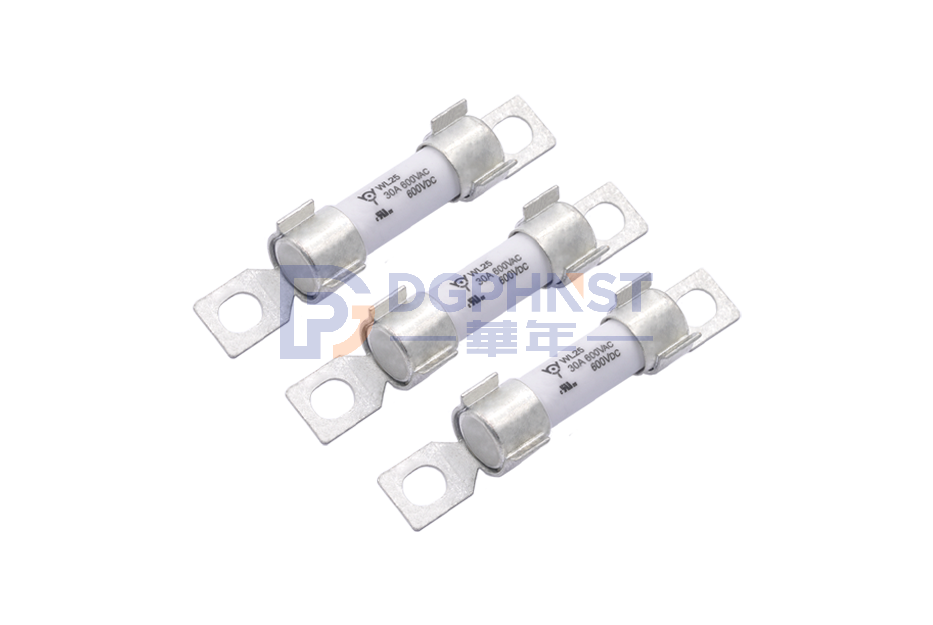
$8.670115
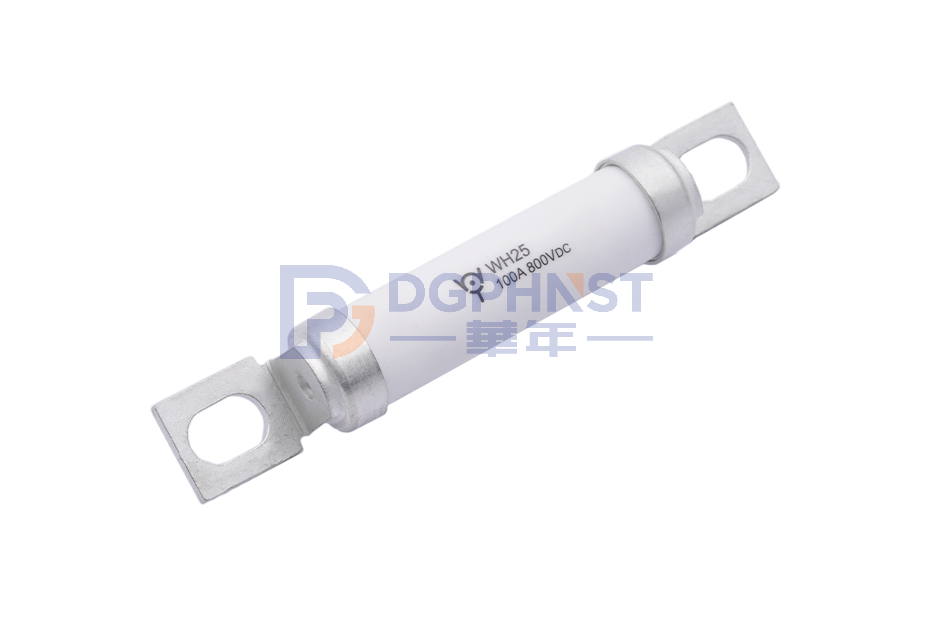
WH25-S100AHBTBTM08BG
Power Fuse ,110*8.5mm ,100A ,800V ,Stud-mount ,WALTER-WH25
$10.081208
WH25-S50AHBTBTM08BG
Power Fuse ,110*8.5mm ,50A ,800V ,Stud-mount ,WALTER-WH25
Introduction:
hnstshop.com/product-list/F08-p1-l10.html" target="_blank" rel="noopener">Power fuses are a common electronic component used to monitor and protect current in circuits. Power fuses are also known as fuses. It plays a crucial role in various applications, effectively preventing circuit overload and faults. This article aims to provide a detailed analysis of the working principle, structure, and application fields of power fuses.
I. Working Principle:
The working principle of a power fuse is based on its overload protection characteristics. When the current in a circuit exceeds the set rated current, the power fuse triggers a protective action by quickly interrupting the circuit and preventing further current flow. This helps protect the circuit and equipment from damage caused by overloads and short circuits.
II. Structure:
Generally, a power fuse consists of the following components:
1. Fuse element: The fuse element is the core part of a power fuse. It is made of a fine wire or strip of metal. When the current exceeds the set value, the fuse element heats up and melts, breaking the circuit and providing protection.
2. Tubular housing: Power fuses are typically enclosed in a housing made of ceramic or glass. These materials offer good insulation properties and high-temperature resistance, enabling them to withstand a certain current and voltage.
3. Terminals: The terminals on the power fuse are used to connect it to the circuit, ensuring the proper flow of current.
III. Application Areas:
Power fuses find wide-ranging applications in various industries and fields, including but not limited to the following:
1. Household electrical: Power fuses are used to protect household circuits, preventing fires and electric shocks caused by appliance overload and short circuits.
2. Industrial control: In industrial control systems, power fuses protect equipment and instruments, ensuring the stable operation of the system.
3. Automotive electronics: Power fuses play a crucial role in automotive circuits, safeguarding vehicle circuits from overload and fault-related issues.
4. Solar and wind energy systems: Power fuses are used to protect circuits in renewable energy systems, ensuring the safety and stable operation of the system.
5. Industrial automation: In industrial automation control systems, power fuses protect motors and equipment, preventing damage from overloads and short circuits.
Conclusion:
Power fuses are essential electronic components with overload protection features, effectively safeguarding circuits and equipment from excessive current and faults. By understanding the working principle, structure, and application areas of power fuses, we can make better choices and use the appropriate fuses to ensure circuit safety and reliability. When using power fuses, it is important to adhere to relevant regulations and follow safe operating practices to ensure their proper functioning and long lifespan.
Note: The above content is for reference purposes only. Specific selection and usage of power fuses should be based on actual circumstances and requirements.