The comparison between the voltage, frequency, and power of Si MOSFET, Si IGBT, GaN MOSFET, and SiC MOSFET is shown in the following figure:
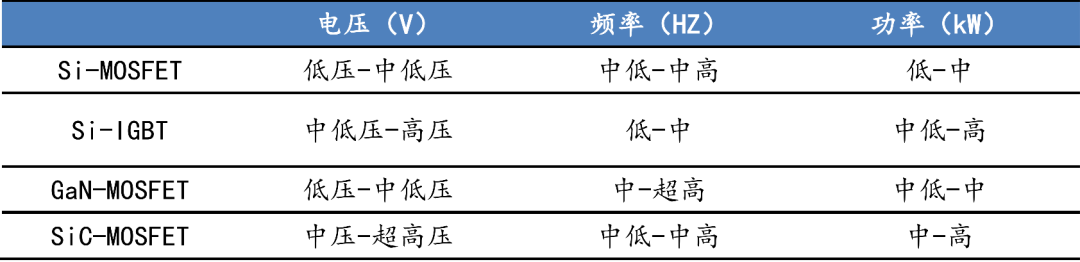
GaN and SiC are highly likely to completely replace silicon-based materials in high-voltage and high-frequency applications
SiC MOSFET focuses on the high-voltage field; GaN MOSFET focuses on the high-frequency field.
Based on the two dimensions of power and frequency, we have sorted out the physical characteristics and applicable scenarios of mainstream power devices:
Although Si IGBT has advantages in the high-voltage field, it is not capable of meeting the requirements in the high-frequency field;
Si MOSFET is capable of handling high-frequency fields, but has certain limitations on voltage;
Compared with MOSFET, SiC perfectly solves the problem of difficult simultaneous implementation of high voltage and high frequency in silicon-based materials. Based on compatibility with high voltage and medium frequency, SiC MOSFET has become the optimal solution for electric vehicles, charging stations, and photovoltaic inverters (without considering cost) due to its high efficiency and small size;
Due to its ultra-high frequency performance, GaN MOSFET has broad prospects in the 5G RF field. Currently, it is mainly used in 5G base station PA and is expected to be expanded to the RF field of terminal devices (such as mobile phones) in the future. In addition, GaN MOsFET also has great potential application value in low and medium voltage fields such as fast charging within 1000V and electric vehicles.


