$0.075727
FSD-F3A15V2T01000BG
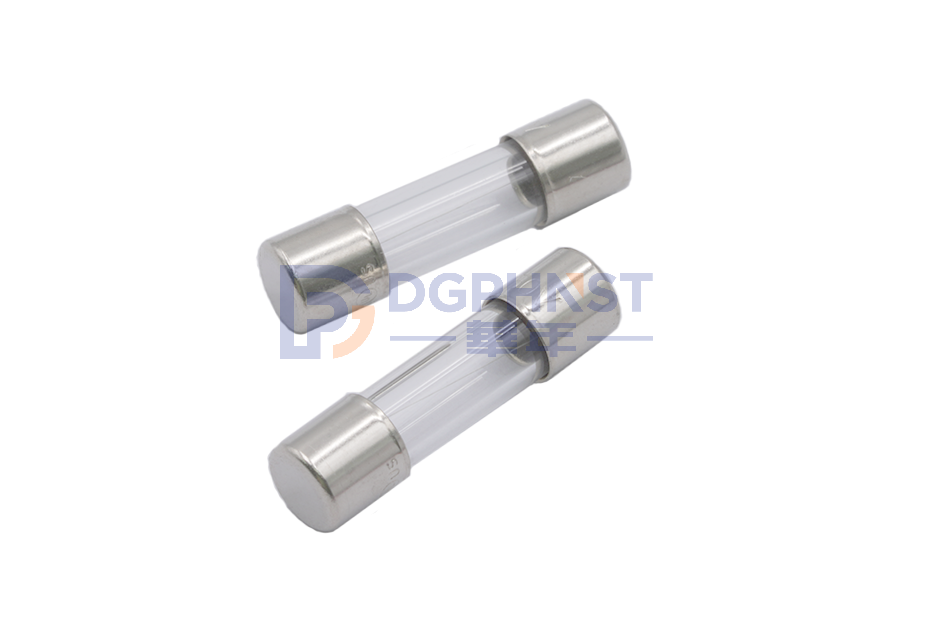
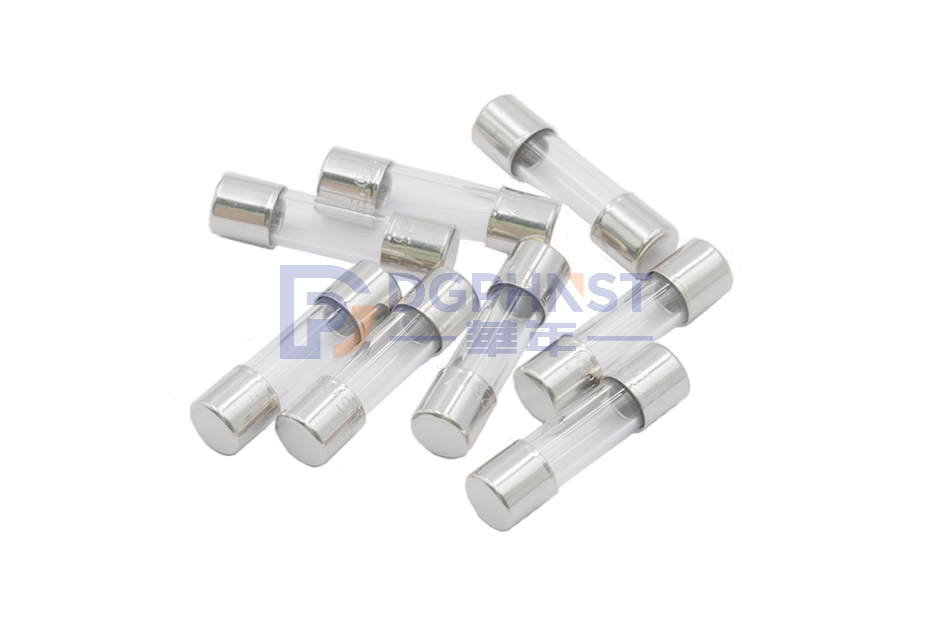
Glass Tube Fuses ,5.2*20 ,3.15A ,250VAC ,Fast Acting Type ,Axial Without Lead ,WALTER-FSD

$0.076636
FSD-F4A00V2T01000BG
Glass Tube Fuses ,5.2*20 ,4A ,250VAC ,Fast Acting Type ,Axial Without Lead ,WALTER-FSD
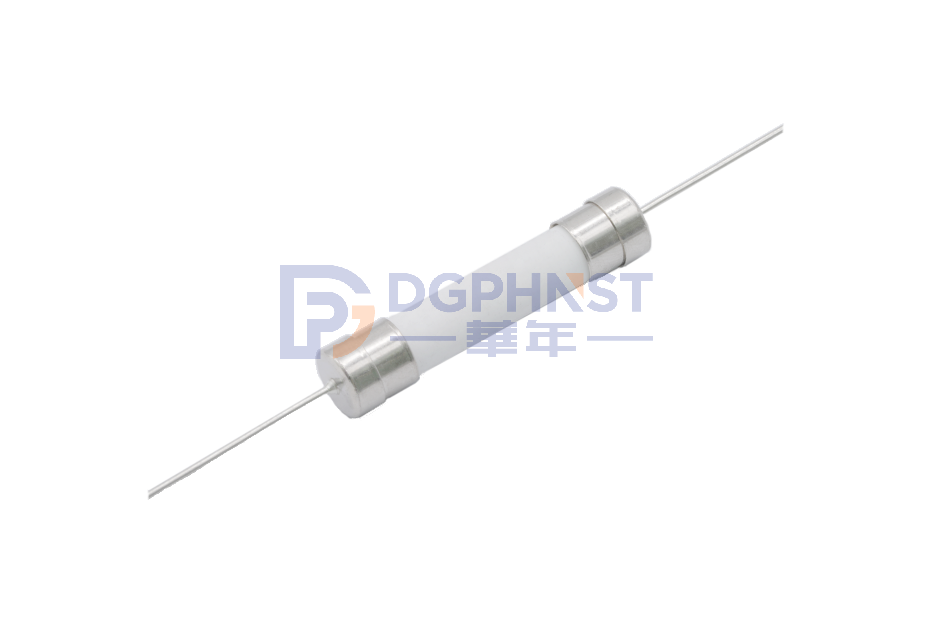
A glass tube fuse is a commonly used electrical protection component known for its safety, ease of detection, and replacement. This article aims to introduce the working principles, structure, and applications of glass tube fuses in various fields.
1. Ceramic tube fuse Working Principles
The working principle of a glass tube fuse is based on its internal fuse wire conductor. When the current in the circuit exceeds the rated current of the fuse, the conductor inside the fuse wire melts, breaking the circuit and providing protection. This mechanism prevents circuit overload and short circuit faults, which can cause equipment damage and safety hazards.
2. Ceramic tube fuse Structure
A glass tube fuse typically consists of the following components:
1. Glass tube: It serves as a protective material, enclosing and safeguarding the internal fuse wire conductor.
2. Fuse wire conductor: Usually made of metal wire, it has a certain resistance and conductivity.
3. Terminals: These are used to connect the fuse to the circuit, ensuring smooth current conduction.
3.Ceramic tube fuse Features and Advantages
Glass tube fuses possess the following features and advantages:
1. Safety and reliability: They can promptly disconnect the circuit in case of circuit overload or short circuit, effectively protecting the equipment and personnel.
2. Easy detection and replacement: The transparent glass tube allows visual inspection of the fuse's condition. If a broken or melted wire is observed, the fuse can be easily replaced.
3. Quick response: Glass tube fuses can rapidly disconnect the circuit when the current exceeds the rated value, providing fast protection.
4. Multiple rated current options: Glass tube fuses are available in various rated current options to meet the protection requirements of different circuits.
4. Ceramic tube fuse Applications
Glass tube fuses are widely used in various fields, including but not limited to:
1. Household circuits: They protect household appliances and devices, preventing circuit overload and short circuit incidents that could lead to fires and safety accidents.
2. Automotive electrical systems: They are applied in automotive circuits to protect the vehicle's electronic devices and wiring from current overload and short circuits.
3. Industrial control systems: Glass tube fuses are used in industrial automation and control systems to protect critical equipment and circuits, ensuring the safe operation of industrial processes.
4. Electronic devices: They are employed in various electronic devices and instruments, providing circuit overload protection and preventing equipment damage and personal injury.
5. Power sector: Glass tube fuses are used to protect transformers, switchgear, and generators in power systems, ensuring the safety of power transmission and distribution.
In summary, glass tube fuses are widely utilized as common electrical protection components with a broad range of applications. Their safety, ease of detection, and replacement make them essential for circuit protection. When selecting and using glass tube fuses, it is important to choose the appropriate rated current and specifications based on specific application requirements and circuit characteristics to ensure the safe operation of the circuit and equipment.