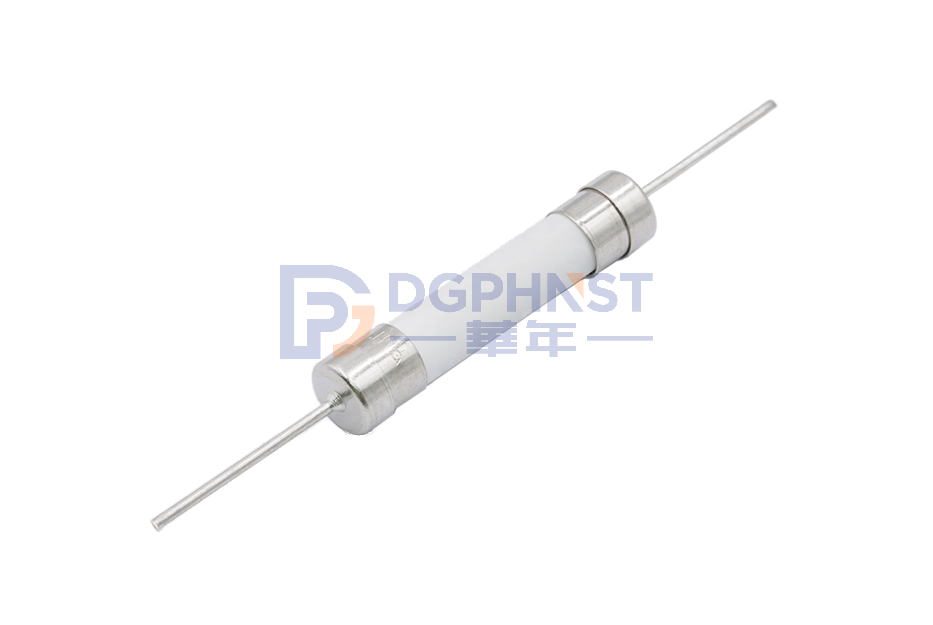
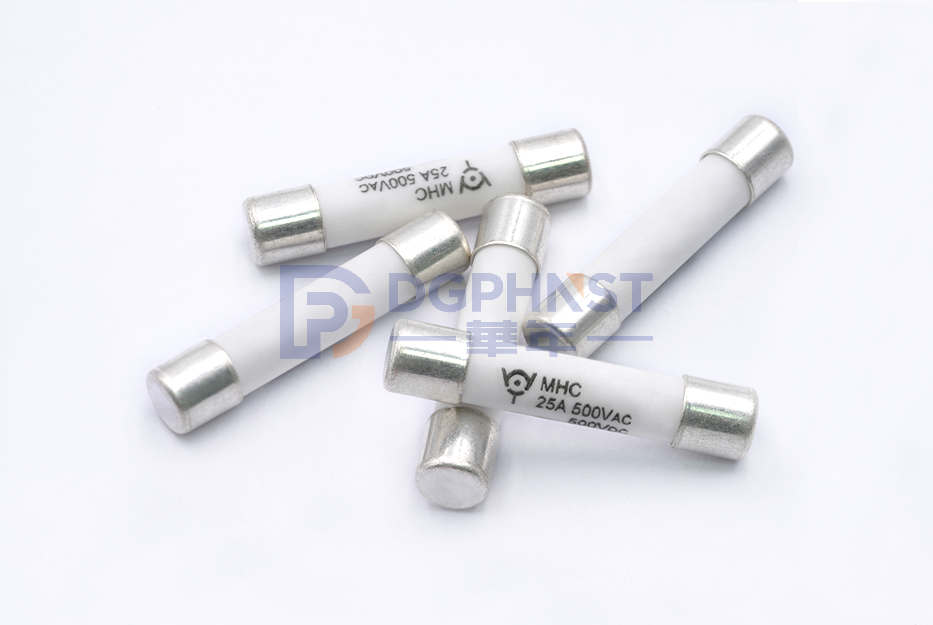
The rated current of the fuse and the fusing current are two different concepts, which respectively represent the current bearing capacity of the fuse in normal operation and abnormal conditions. The rated current refers to the maximum current value of the fuse under specific conditions for a long time without blowing, and the blown current refers to the maximum current value of the fuse in a short period of time and eventually cause it to blow.
Rated Current (Rated Current) refers to the maximum current that the fuse can withstand for a long time under normal operating conditions, and the fuse is marked with an In mark. This value is measured at a specific ambient temperature, 25°C for practical use, and the ambient temperature is higher or lower than 25°C, so that the rated current is adjusted accordingly according to the actual ambient temperature. For example, if the ambient temperature increases, the carrying capacity of the fuse will decrease, so it seems to choose a fuse with a higher rated current to ensure its normal operation.
Melting Current refers to the maximum current that a fuse can withstand for a short period of time and eventually cause it to blow. This value is greater than the rated current, because in the event of an abnormal circuit (such as a short circuit), the fuse quickly blows to protect the circuit from damage. The specific value of the fusing current depends on factors such as the material, structure and size of the fuse.
When choosing a fuse, in addition to considering its rated current and fusing current, the following factors should also be considered:
Ambient temperature: The ambient temperature will affect the performance of the fuse, choose the appropriate fuse according to the actual working environment.
Rated voltage: The rated voltage of the fuse should be equal to or greater than the operating voltage of the circuit to avoid damage to the circuit caused by the high voltage generated when the fuse is blown.
Working mode: Select the appropriate type of fuse according to the working mode of the circuit (such as continuous or intermittent working).
Safety certification: Select fuses that meet local safety standards, such as UL and VDE.
Breaking capacity: The breaking capacity of the fuse should be large enough to ensure safe fusing under abnormal conditions such as short circuit.
The rated current and fusing current of the fuse are the two core technical parameters, which jointly determine the protection function of the fuse in the circuit. The correct selection and use of fuses can ensure the safe operation of the circuit. When selecting fuses, consider a variety of factors to ensure that the fuses can have their due protection when necessary.



