Voltage polarity and symbol rules of MOS transistors
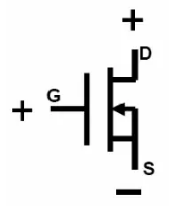
The above figure shows the symbol of an N-channel MOS transistor. D represents the drain, S represents the source, G represents the gate, and the arrow in the middle indicates the substrate. If the arrow is pointing inward, it indicates an N-channel MOS transistor, and if it is pointing outward, it indicates a P-channel MOS transistor.
In the actual production process of MOS transistors, the substrate is connected to the source before leaving the factory, so in the symbol rules; The arrow representing the substrate must also be connected to the source to distinguish between the drain and source.
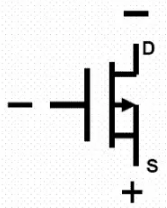
The above figure shows the symbol of a P-channel MOS transistor.
The polarity of the applied voltage of MOS transistor is the same as that of our ordinary transistor. The N-channel transistor is similar to an NPN transistor, with the drain D connected to the positive electrode and the source S connected to the negative electrode. When the gate G is at a positive voltage, a conductive channel is established, and the N-channel MOS transistor starts working.
A PNP transistor with the same P channel, where the drain D is connected to the negative electrode, the source S is connected to the positive electrode, and the gate G is at a negative voltage, establishes a conductive channel and the P channel MOS transistor begins to operate.
